| Research topics: |
 |
(1) |
Models for material circulation, water quality evaluation |
|
Related instructor(s): Akio OKAYASU |
|
Outline: |
This research attempts to evaluate water quality and ecological systems by a material circulation model in the nearshore movement. The role of bivalves is also studied, and the research aims to develop a performance index for ecosystems and nearshore environments that combines all of these factors. Studies of benthos in Kashimanada and observations of water quality in Tokyo Bay have been also started. |
|
 |
|
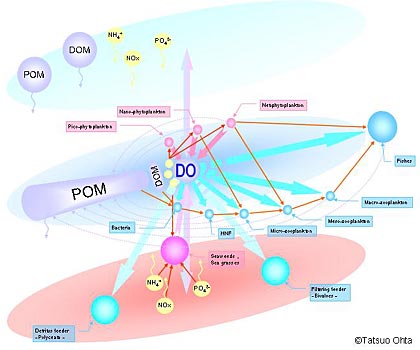
Figure 1. Conceptual diagram of a phosphorus-base material circulation model. Upper level represents the surface layer, the middle level seawater, and the lowest level the earthen seabed. Arrows indicate the flow of material. |
 |
 |
(2) |
Development of a numerical model for waves and currents in coastal and near-shore areas |
|
Related instructor(s): Akio OKAYASU |
|
Outline: |
This research topic develops a numerical model for waves and currents in surf zones, shallow water areas, and inland bays, to evaluate beach topography change, wave forces on coastal structures and material circulation in the nearshore areas. The research is also applied to numerical simulation for the artificial upwelling flows. |
|
 |
|
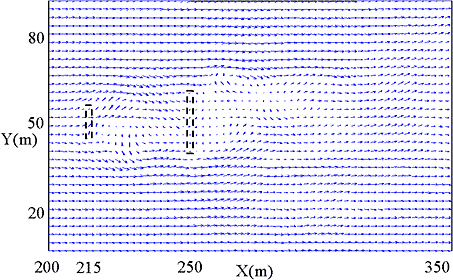
Figure 2. Calculation of non-stationary upwelling flows caused by duplex screen-like structures using an LES numerical model. Diagram shows flow pattern from above. The alternate generation of vertical eddies due to the screen panels can be seen. |
 |
 |
(3) |
Clarification of fluid motion and bottom sediment movement in the surf zone |
|
Related instructor(s): Akio OKAYASU |
|
Outline: |
In order to predict detailed fluid motion and topographical changes in the vicinity of seabed due to breaking waves, this research takes a multidirectional approach that includes laboratory experiments, full-scale tests, on-site observations, and numerical simulations. |
|
 |
|
Figure 3. On-site observation of flow field in the surf zone and suspended sediment concentration in Kashimanada beach.
The relationship between fluid motion and sediment suspension due to breaking waves are investigated through data obtained by wave gages, velocimeters, and suspended sediment concentration meters. |
 |
 |
(4) |
Developing environment-improving structures to control nearshore waves |
|
Related instructor(s): Akio OKAYASU |
|
Outline: |
The research topic aims for development and evaluation of structures that consider the environment and use of coastal and near-shore areas. This includes the development of wave control structures that improve water quality in small-to-medium-sized ports such as fishing harbors, and the evaluation of flow conditions around concrete blocks in order to investigate the potential of coral anchoring. |
|
 |
|
Figure 4. Experiment on water exchange breakwater in a wave flume. A tube was constructed in the lower part of the breakwater body, and factors such as the rate of water exchange and the level of calmness in the harbor were investigated.
The research also attempts to improve efficiency by using creative ideas in the design of the inlet-outlet openings. |